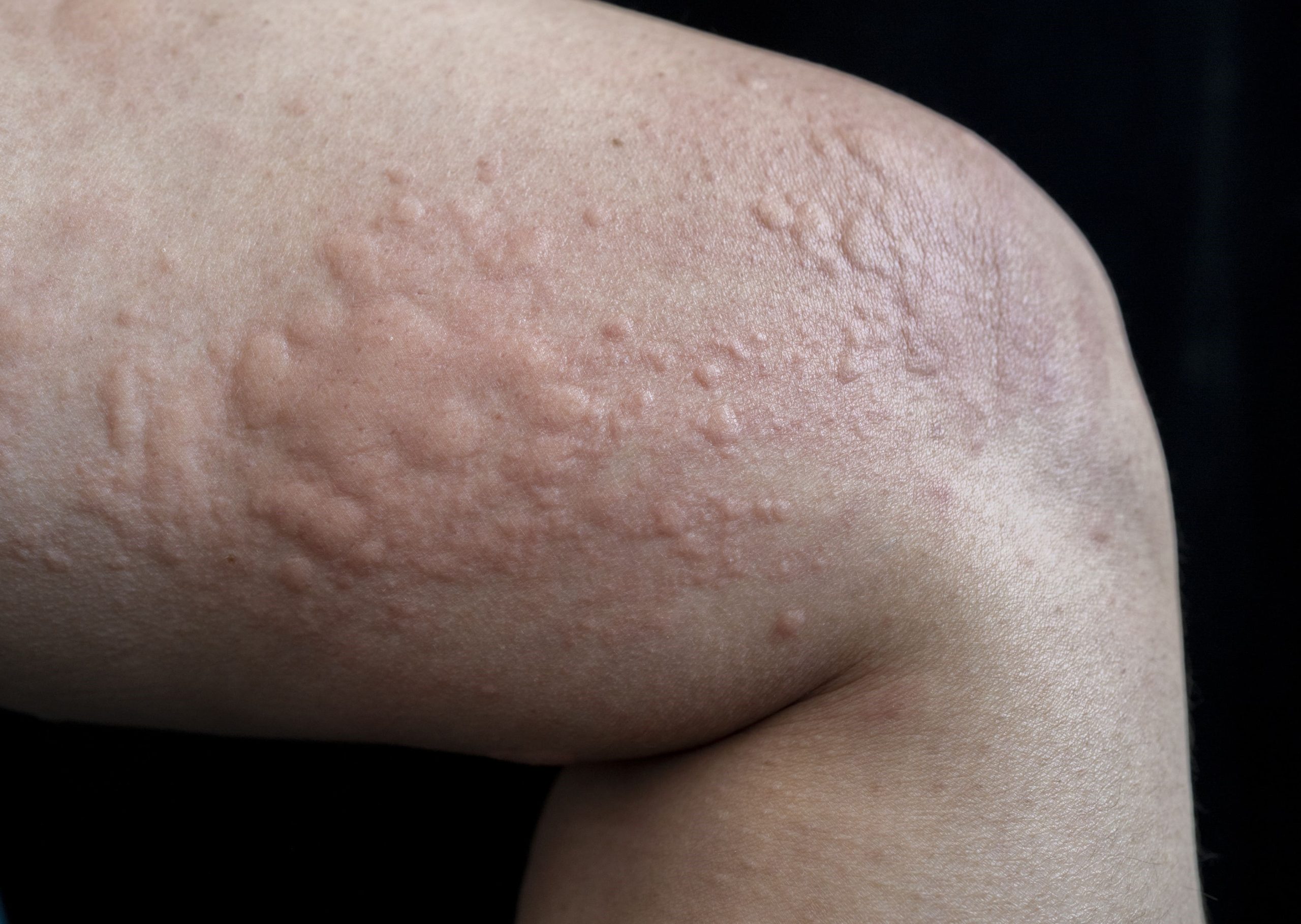
Chronic hives, also known as chronic urticaria, is a condition where itchy, red welts persist for six weeks or longer, often without an identifiable trigger. Unlike acute hives, which usually resolve quickly, chronic hives require consistent management to control symptoms effectively. While the exact cause remains uncertain, treatment plans often focus on alleviating discomfort and preventing further flare-ups. Below will explore some of the most common treatment approaches.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines serve as the first defense against chronic hives. These medications block histamine, a chemical the body releases during an allergic reaction that triggers itching and swelling. Non-drowsy antihistamines, like cetirizine, loratadine, or fexofenadine, ease symptoms without causing heavy sedation.
If a single daily dose does not control symptoms, doctors may increase the dosage, sometimes up to four times the usual amount, with careful supervision. They may also combine different types of antihistamines to enhance effectiveness. These treatments offer relief and remain safe for long-term use under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are sometimes prescribed for individuals with severe hives that do not respond to antihistamines. These medications reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system’s overactivity, helping control chronic hives’ more aggressive symptoms.
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are typically used short-term to avoid potential side effects associated with long-term use. Prolonged use can lead to complications such as weight gain, high blood pressure, and bone density loss. For this reason, they are only used when other treatment options are insufficient and the benefits outweigh the risks.
Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressants may be introduced into the treatment plan when antihistamines and corticosteroids do not relieve symptoms. These medications work by modulating the immune system to prevent the body from overreacting and triggering hives. Options like cyclosporine or omalizumab (commonly marketed as Xolair) have shown promise in managing chronic hives. Omalizumab is a biological therapy that targets specific antibodies involved in the body’s allergic response, making it a targeted option for severe cases. Immunosuppressants often require careful monitoring due to potential side effects, including an increased risk of infections or interactions with other medications.
Other Approaches to Managing Hives
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments may help minimize flare-ups. Some individuals can prevent symptoms by avoiding triggers such as certain foods, stress, or extreme temperatures. Keeping a detailed diary to track potential triggers helps understand what might contribute to outbreaks. Managing symptoms often requires a combination of approaches for patients with chronic hives with no identifiable cause. Working closely with a healthcare provider, such as an allergist or immunologist, helps make sure that treatment is tailored to individual needs and adjusted as necessary.
Consult a Specialist for Chronic Hives Management
Managing chronic hives often requires a comprehensive approach. Treatment typically starts with antihistamines, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants for more severe cases. Working with an allergist or immunologist is key to finding effective symptom relief. With the proper treatment and monitoring, patients can reduce flare-ups and improve their quality of life. New therapies like omalizumab offer hope for those with severe or unresponsive hives. Consult a specialist to create a personalized plan that works for you. Schedule an appointment with a certified allergist or immunologist today.
Keep an eye for more latest news & updates on Bangkok Tribune!